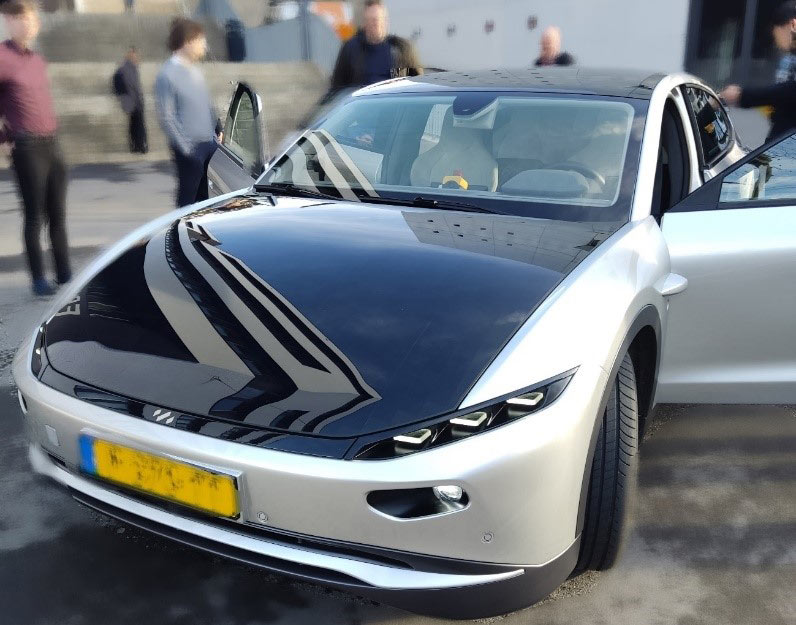
Article image: Example of VIPV in a car: Lightyear prototype One Vehicle-Integrated Photovoltaics (VIPV) is seen as a revolutionary opportunity to reduce the environmental impact of the transport sector and improve public health. This technology involves integrating photovoltaic (PV) modules directly into the structure...
Over the past decade, the development of solar cells has been significantly influenced by semiconductors known as hybrid perovskites. These materials have sparked intense interest within the scientific community due to their ease of processing and the high efficiency they enable under various irradiation...
Today, renewable energies are the only available technology that can lead the energy transition towards a more sustainable society. Among these technologies, solar photovoltaic energy stands out especially, due to the vertiginous increase it has experienced in recent years as a result of its...
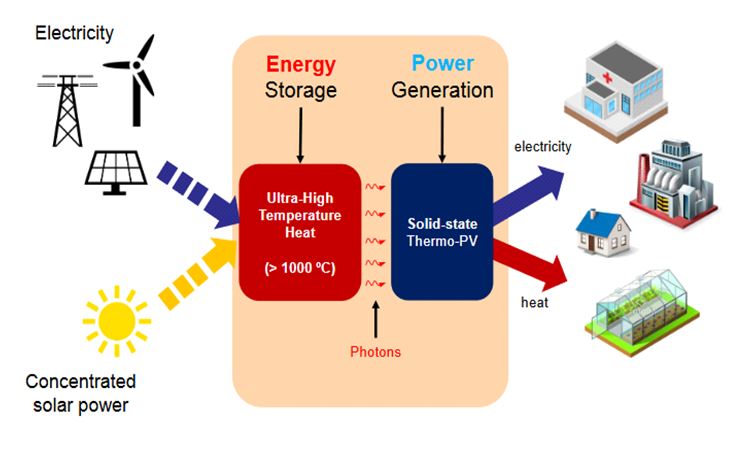
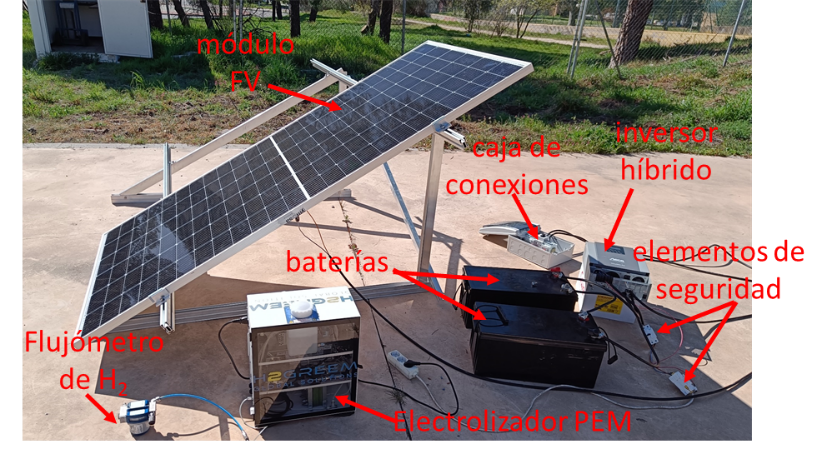
Hydrogen is considered an energy carrier capable of transporting and storing energy for subsequent use in a wide range of applications, from electricity production to transportation and industry. The most common method for hydrogen production today is natural gas reforming, which utilizes methane obtained...
Around 95% of the current production of photovoltaic (PV) modules is based on silicon wafers, which need to be extremely pure so that high efficiencies can be achieved when processed as solar cells. Silicon PV technology begins with the carbothermic reduction of quartz in...
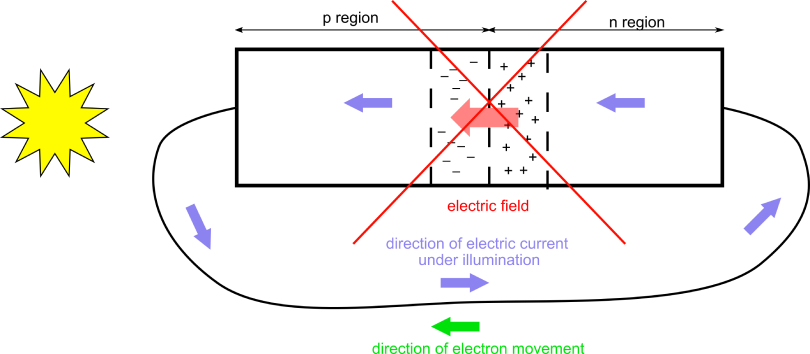
The photovoltaic effect refers to the experimental observation of a voltage arising as a result of light shining on a system. The most common observation of this phenomenon occurs in the context of solar cells, where it is used to extract electrical energy from...
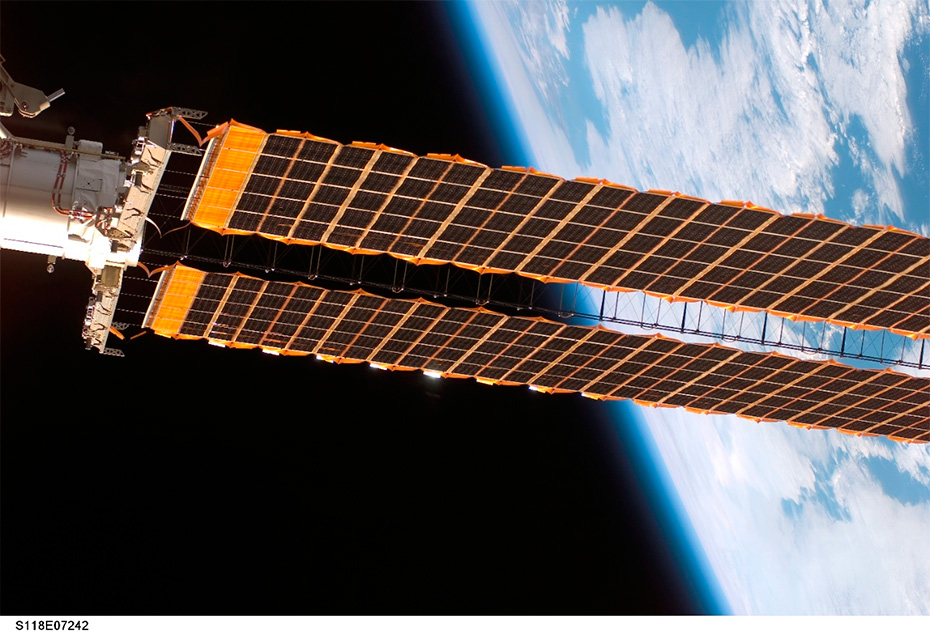
It is fair to say that the first great success of photovoltaic solar energy occurred in outer space. In 1958, the Vanguard I satellite – the third human device put into Earth orbit after Sputnik 1 and 2 – was equipped with modest solar...
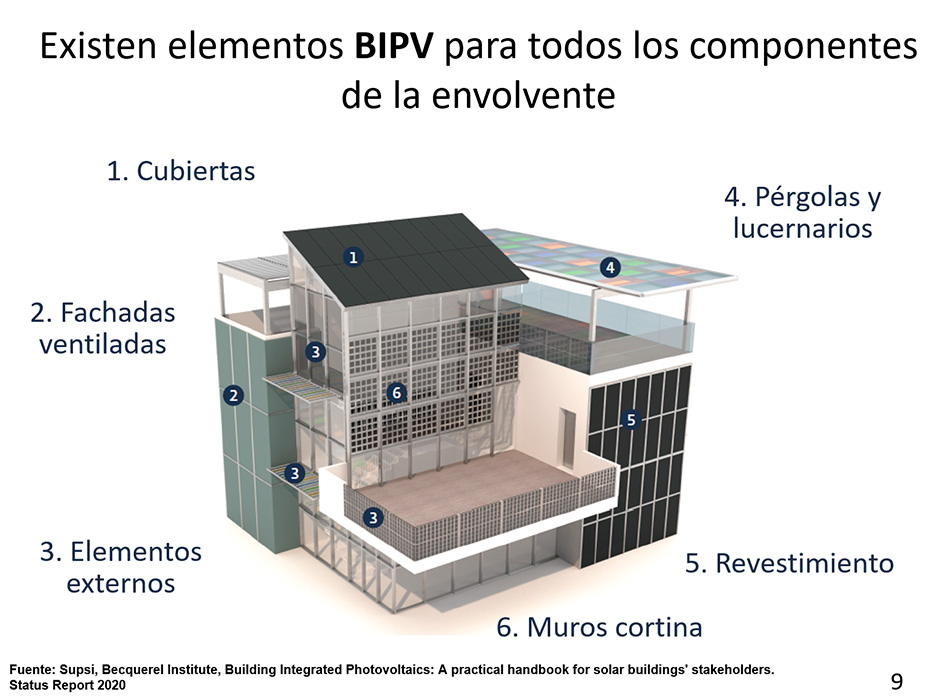
In the era of the search for sustainability, architecture and energy must go hand in hand if buildings are to play a key role in the transition towards new city models. Today, the idea that optimizing a building’s energy performance is a constraint on...
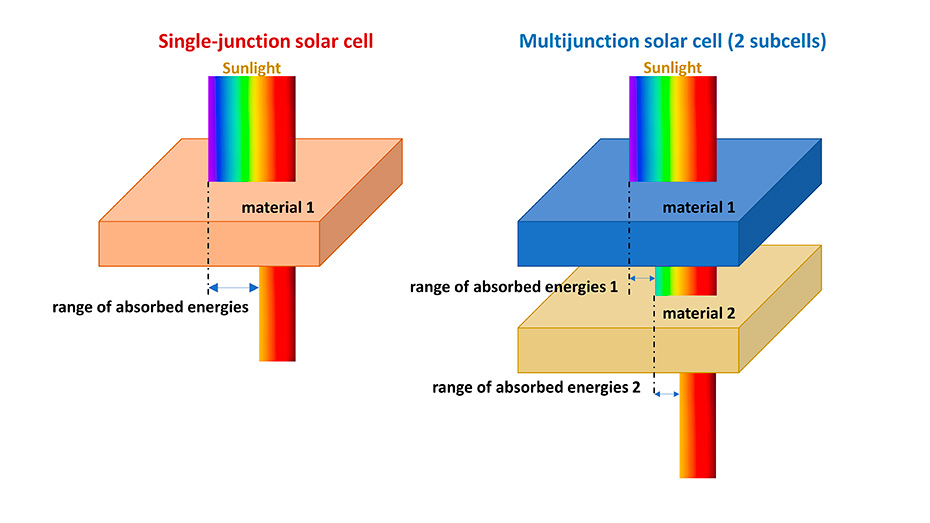
Multijunction solar cells were invented to mitigate a fundamental loss source in the conversion of light to electricity. To understand this kind of loss we have to consider these two facts: Semiconductor materials used to fabricate solar cells are characterized by their bandgap, which...
The term thin-film solar cell, or second-generation solar cell, refers to a particular type of photovoltaic (PV) device whose main characteristic is the reduced amount of active material required to manufacture efficient cells. Probably best expressed by Ken Zweibel in 2004: “the fundamental idea...